Fiberglass is widely used in the field of electronics and electrical due to its good insulation and corrosion resistance.
Specific applications include:
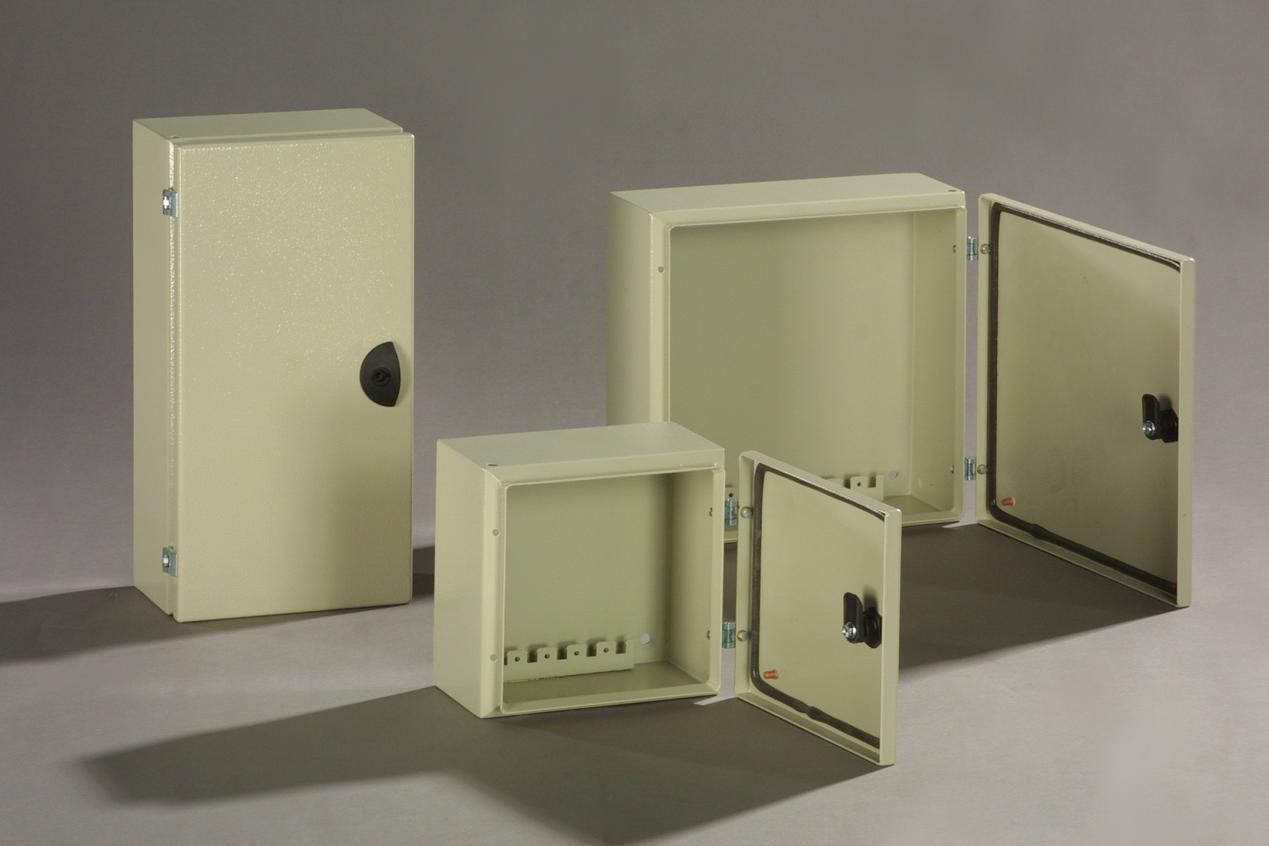
Electrical enclosures: Such as electrical switch boxes, wire boxes, instrument panel covers, etc.
Electrical and electronic components: such as insulators, insulating tools, motor end covers, etc.
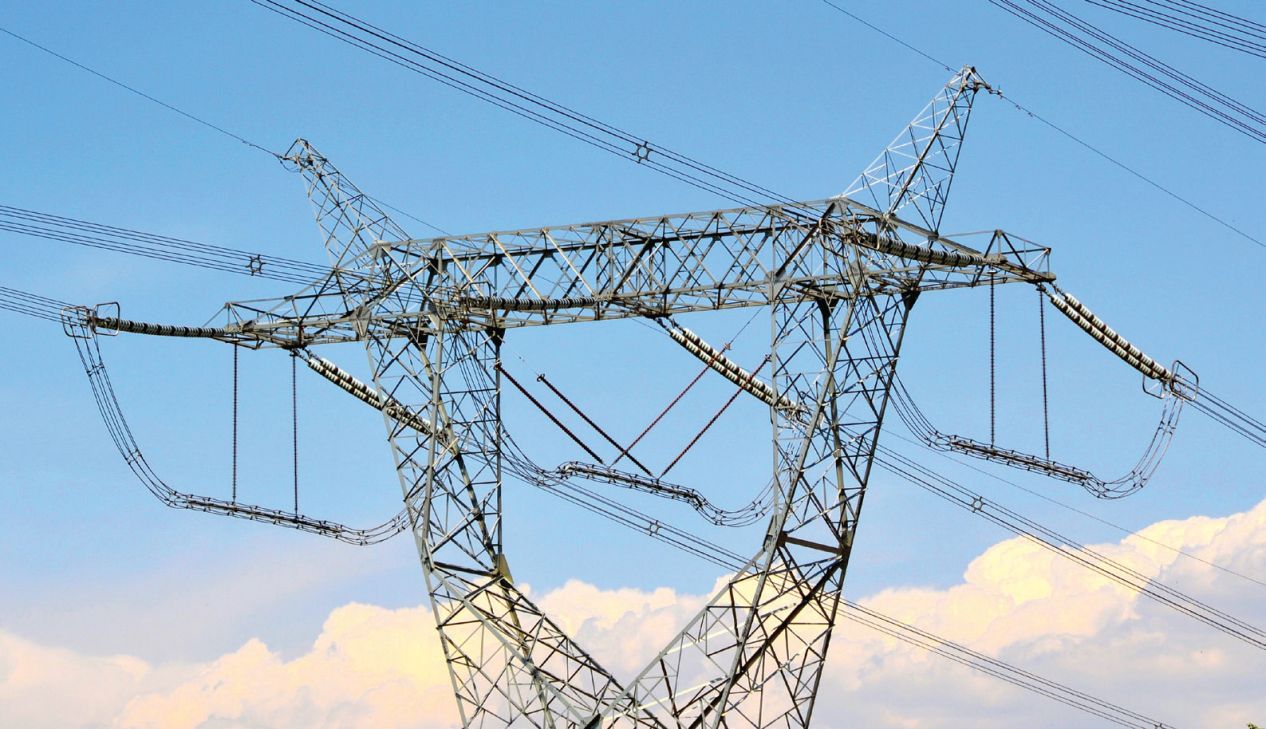
Transmission lines: including composite cable brackets, cable trench brackets, etc.
In addition to insulation and corrosion resistance, glass fiber has the following advantages in the field of electronics and electrical:
Lightweight and high strength: Glass fiber has low density but high strength, which can reduce the weight of electronic equipment while ensuring structural strength. This is especially important for electronic products that need to be portable or miniaturized.
High temperature resistance: Glass fiber has a high heat deformation temperature and can withstand the high temperature generated when electronic components are working, ensuring the normal operation of electronic equipment in high temperature environments.
Good dimensional stability: Glass fiber has a low thermal expansion coefficient, which can ensure the dimensional stability of electronic components when the temperature changes, and improve the accuracy and reliability of electronic equipment.
Easy to process: Glass fiber can be compounded with various resins and made into various complex-shaped parts through molding, winding and other processes to meet the diverse design requirements of electronic equipment.
High cost-effectiveness: Compared with other high-performance materials, glass fiber has a relatively low cost, which can reduce the manufacturing cost of electronic equipment.
In short, glass fiber has been increasingly widely used in the field of electronics and electrical due to its excellent comprehensive performance. It is an ideal material for manufacturing high-performance, lightweight and low-cost electronic equipment.
Compared with other materials, the advantages of glass fiber in the field of electronics and electrical are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Lighter weight: Compared with metal materials, glass fiber has a lower density, which means that electronic components and housings made of fiberglass will be lighter, which is particularly important for weight-sensitive fields such as mobile devices and aerospace.
2. Excellent insulation performance: Glass fiber is an excellent insulating material with much higher electrical insulation than metal. It can effectively prevent circuit short circuits and leakage, and improve the safety and reliability of electronic equipment.
3. Strong corrosion resistance: Unlike metal, glass fiber is not affected by environmental factors such as moisture, acid and alkali, and has extremely strong corrosion resistance. It can work stably for a long time in harsh environments and extend the service life of electronic equipment.
4. Higher design freedom: Glass fiber can be compounded with various resins and easily processed into various complex shapes through molding, winding and other processes, giving designers greater design freedom and meeting the development trend of miniaturization, lightweight and integration of electronic equipment.
5. Obvious cost advantage: Compared with other high-performance materials such as ceramics, the manufacturing cost of glass fiber is lower, which can effectively reduce the production cost of electronic equipment and improve product competitiveness.
In short, glass fiber plays an indispensable role in the field of electronics and electrical with its excellent comprehensive performance and cost advantages, and its application scope will continue to expand with the advancement of technology.
Compared with other insulating materials, glass fiber has a significant cost advantage. Specifically:
Lower cost than high-performance materials: Compared with high-performance insulating materials such as ceramics and polytetrafluoroethylene, the raw material and manufacturing costs of glass fiber are relatively low, so it has a price advantage.
Close to the price of some traditional materials: Compared with some traditional insulating materials, such as plastics and rubber, the price of glass fiber may not be much different, or even slightly lower.
Lower long-term use cost: Glass fiber has good durability and a long service life, which means that in the long-term use process, the cost of replacement and maintenance can be reduced, further improving its cost-effectiveness.
However, it should be noted that the specific price of glass fiber will be affected by many factors, such as:
Types and specifications of glass fiber: The prices of different types and specifications of glass fiber will vary.
Market supply and demand: Factors such as raw material price fluctuations and changes in market demand will also affect the price of glass fiber.
In general, in most cases, glass fiber has a high cost-effectiveness and is one of the most widely used insulating materials in the field of electronics and electrical.
Compared with other insulating materials, fiberglass has mixed environmental performance:
Advantages:
Recyclable: Fiberglass can be recycled and reused, reducing the consumption of virgin resources. Some manufacturers have begun to use recycled glass to produce fiberglass, further reducing the impact on the environment.
Long service life: Fiberglass has good durability and a long service life, which can reduce the frequency of material replacement, thereby reducing the overall impact on the environment.
Asbestos-free: Modern fiberglass materials no longer use asbestos as a reinforcing material, avoiding the harm of asbestos to human health and the environment.
Disadvantages:
Energy consumption in the production process: The production process of fiberglass consumes a lot of energy, which will produce certain carbon emissions.
Some products use resin: Resin is added to some fiberglass products to enhance their performance, and the production and degradation process of resin may have a negative impact on the environment.
Recycling rate needs to be improved: Although fiberglass can be recycled, the actual recycling rate is still low, and a large amount of discarded fiberglass still puts pressure on the environment.
Summary:
In general, glass fiber is not an absolutely environmentally friendly material, but compared with some traditional insulation materials, it still has certain advantages in environmental performance. With the advancement of technology and the improvement of environmental awareness, it is believed that more environmentally friendly glass fiber materials and recycling technologies will appear in the future to further reduce its impact on the environment.
Our fiberglass raw materials are as follows: