Advantages of Panel Glass Roving
- High Strength and Durability: Panels reinforced with glass roving are robust and can withstand significant stress and impact.
- Lightweight: These panels are much lighter compared to traditional materials like metal, making them ideal for applications where weight savings are crucial.
- Corrosion Resistance: Glass roving panels do not corrode, making them suitable for use in harsh environments, such as marine and industrial applications.
- Versatility: They can be molded into various shapes and sizes, offering flexibility in design and application.
- Thermal Insulation: Composite panels can provide good thermal insulation properties, making them suitable for building applications.
Common Uses
- Construction: Used in building facades, cladding, and structural components.
- Transportation: Employed in vehicle bodies, panels, and parts for cars, boats, and aircraft.
- Industrial: Utilized in equipment housings, piping, and tanks.
- Consumer Goods: Found in sports equipment, furniture, and other durable consumer products.
Product Specification
We have many types of fiberglass roving: fiberglass panel roving, spray-up roving, SMC roving, direct roving, c-glass roving, and fiberglass roving for chopping.
| Model |
E3-2400-528s |
| Type of Size |
Silane |
| Size Code |
E3-2400-528s |
| Linear Density (tex) |
2400TEX |
| Filament Diameter (μm) |
13 |
| Linear Density (%) |
Moisture Content |
Size Content (%) |
Breakage Strength |
| ISO 1889 |
ISO3344 |
ISO1887 |
ISO3375 |
| ± 5 |
≤ 0.15 |
0.55 ± 0. 15 |
120 ± 20 |

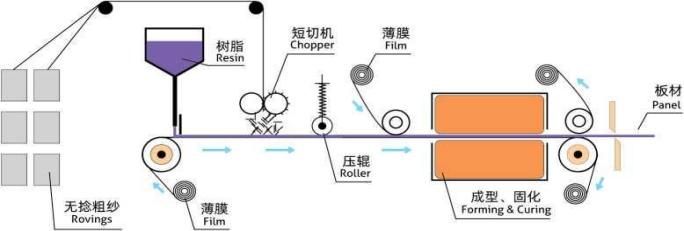
Manufacturing Process of Panel Glass Roving
- Fiber Production:
- Glass fibers are produced by melting raw materials like silica sand and drawing the molten glass through fine holes to create filaments.
- Roving Formation:
- These filaments are gathered together to form roving, which is then wound onto spools for use in further manufacturing processes.
- Panel Production:
- The glass roving is laid into molds or onto flat surfaces, impregnated with a resin (often polyester or epoxy), and then cured to harden the material. The resulting composite panel can be customized in terms of thickness, shape, and surface finish.
- Finishing:
- After curing, the panels can be trimmed, machined, and finished to meet specific requirements, such as adding surface coatings or integrating additional components.